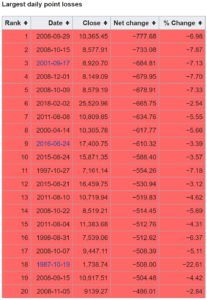
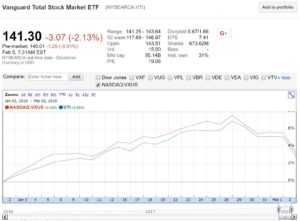
Last Friday there was blood flowing down Wall Street. The Dow suffered its 6th largest point drop in a single day, falling 666 points (que Iron Maiden). Being a top 10 worst day seems like it’s important, but that really overstates things. The Dow is so high now, at 26,000, that a 700-odd point drop really isn’t that big.
If you look at the list of the Top 20 biggest point drops, this one ranks at #6. But in percentage terms it’s lowest on that list. In fact, since 1950 there have been about 200 or so drops in percentage terms this bad. That comes to about 2-3 per year. So let’s not get too freaked out.
Also, let’s keep in mind that the stocks are up 3% so far for the year. That’s really good, and no one would normally complain about that after just a month. But it’s human nature to complain, so that’s what we do.
OK, I’m a little calmer. But it’s still worth trying to figure out why the drop happened. Most economists look to the Federal Reserve as the culprit. Or more precisely the idea that inflation is steadily rising and that will prompt the Fed to start raising interest rates. You know my feelings on inflation in general, and specifically I predicted a few weeks back that over the long term we would have really low interest rates. Either way, new ideas on inflation weren’t what spooked the market, but the idea that the Fed would start raising interest rates.
That begs the question, how do interest rates impact the market? And that’s really French for Why is the Fed so important.
How does the Fed impact the economy?
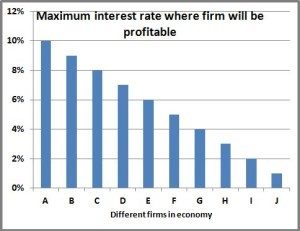
Let’s imagine a really simple economy. There are ten companies named A and B and C all the way down to J. Just like in real-life, not all companies are created equal, with some being much more profitable than others. Here A is the most profitable (maybe like Apple) while J is the least profitable (maybe like JC Penney).
Interest rates will play a big part in the profitability of these firms. As interest rates go up, the amount they spend on interest for all their debt goes up as well. Because A is so profitable, it would only start to lose money if interest rates went really high, up over 10%; however J is much more vulnerable and will become unprofitable if interest rates go over 1%. All the other companies have a similar situation as shown in the graph.
So this is where the Fed comes in. Let’s say the Fed sets the interest rate at 6%. Firms A, B, C, D, and E are all profitable even when the interest rates are that high; but firms F, G, H, I, and J are not. Because of that things won’t look good for firms F-J. Maybe it’ll be so bad that they’ll go bankrupt or maybe they’ll lay off people or put a hiring freeze on.
At 6% interest, you have five firms that are doing well (A-E)—growing, hiring more people, expanding, etc.—and five that aren’t (F-J). And at 6% the economy is performing at a certain level. But what would happen if the Fed lowered the interest rate from 6% down to 5%? One more firm (F) would be profitable, and in general it would benefit all the firms. The profitable ones would be doing even better, and the unprofitable ones wouldn’t be quite so bad off. And that would lead to a strong economy: more “stuff” would be produced and more people would be employed.
So there is very clear relationship that lower interest rates led to a stronger economy. Having a strong economy is one of the Fed’s goals, so that begs the question, “Why doesn’t the Fed push rates all the way down to 0%?”
This is where it starts to get interesting. It’s my favorite topic: Inflation. Remember that the Fed’s first job is to control inflation. Let’s look at the Fed’s decision to move interest rates from 6% to 5%, but now look at it with an eye towards inflation.
In our pretend world, let’s assume at 6% interest rates the economy is doing well. Things are growing and unemployment is fairly low. When interest rates go to 5%, firm F will become profitable so they’ll want to hire some people—makes sense. But remember that unemployment is low, so F is going to need to tempt people who are already working for A or B or C or whoever to come work at F. How does F do that? They pay them more.
F starts to pay people more, but A doesn’t take this lying down, so A starts paying more. This wage increase trickles through the economy. But A and B and even F need to make money, so the increase in compensation they’re paying to their employees gets passed along to consumers in the form of higher prices. When prices start rising, that’s INFLATION. And controlling inflation is the Fed’s #1 goal. So that creates the difficult balance for the Fed—they want the economy to do well but not so well that it triggers inflation.
So there you go. You just completed a course in “Introductory Macroeconomics”.
What’s going on today?
Now that you have that little lesson under your belt, how does that relate to what’s going on with the Fed right now? Currently, the Fed has interest rates at about 1.5%. That’s really low, but actually over the past couple years the Fed has been raising interest rates from when it was at 0%. Obviously that’s super low, so shouldn’t the Fed be worried about inflation?
Remember the circumstances of how interest rates got that low. At the beginning of 2008 the economy was going strong and the interest rate was at over 5%. But then the financial crisis hit, blowing up the banking industry, and sending the world economy into a very sharp recession. A ton of people lost their jobs (unemployment went up) so prices stayed flat or even started to fall a little bit.
With all this going on, the Fed threw a life raft to the economy in the form of near 0% interest rates. In the intervening years, the economy has rebounded and unemployment has fallen, but inflation has remained pleasantly low. This is kind of the best of both worlds for the Fed—the economy is strong and there’s no inflation. The two things they have to balance are both in happyland, so they have kept interest rates low.
But what keeps them in the news is “the specter of inflation on the horizon.” If you follow this stuff (like I do) in the past few months, every time inflation numbers come out, everyone looks at those and tries to predict what the Fed will do.
Every time this happens the market swings like a pendulum. If rates are going to go up, the stock market gets crushed because firms will be less profitable (as we saw on Friday and in the little illustration above). If that changes and we think rates are going to stay low, the market shoots up like a rocket.
What does it really mean when the Fed changes interest rates?
With all of this, are we just a bunch of idiots? Should we really be so happy if the Fed is keeping rates low, and should we be so bummed if the Fed raises rates?
As the parent of two boys who one day may start sponging off Foxy Lady and me, I think the parent-child relationship is a good analogy.
Imagine you have parents (the Fed) who have a grown child (the US economy). Times are tough for the child (the economy is doing poorly) so the parents help out (the Fed lowers interest rates). The good scenario is that the child starts doing better to the point where he doesn’t need his parents’ help (the economy strengthens so it can withstand higher interest rates). The bad scenario is the child becomes dependent on his parents’ help and is never able to make it on his own.
In this analogy the parents reducing the amount of help they give (the Fed raising rates) is a good thing, isn’t it? It means that the kid is getting things on track and is standing on his two feet. For this reason, I actually think it’s a good thing if the Fed raises interest rates because it means that the economy is strong enough that it doesn’t need insanely low interest rates any more. Yet the markets react in the exact opposite direction.
I get it. Just as the kid would be bummed if the parents said, “Hey pal, since you’re starting to make some money now, we won’t be sending those monthly checks”, the companies are bummed that they can’t borrow money so cheaply. But that isn’t sustainable.
I chalk this up to yet another of a million examples of how the stock market acts in a goofy manner in the short term. And another reason why I NEVER try to time the market. I just keep my head down and invest for the long term, regardless of what is going on with interest rates. But watching everyone hang on the Fed’s every last word does make for perverse entertainment.

One thought to “Fed rate hike spooks Wall Street”